
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has many inspiring applications, however, self-driving cars or autonomous vehicles (AV) is probably the most exciting one. It will be a true game changer and affect almost every person on the planet.
Due to an exponential increase in processing power among other factors, the past decade has seen a huge increase in AI research & development. One of the recent technologies enabled by this AI bonanza is bots: they can now play video games better than humans. But at the end, it is the self-driving car which can be seen as the AI killer application — and major technology and automobile companies are working on solutions to bring AVs on the street.
Seeing the exciting developments in self-driving vehicles like the self-driving feature of Teslas, parking summoning features, or the automated driver safety features of Mercedes, people have a well-defined vision of what a future with Autonomous Vehicles would look like. Other than these obvious advantages, there are also unseen advantages, which draw more commercial interests.

One of these industries is that of long-haul trucking. Long-haul trucking involves the delivery of good over large distances (>250 miles) between manufacturing plants, retail stores or distribution centers.
However, it’s a dangerous job, with the work involving health risks for the drivers, and the necessity of timely delivery of goods increasing work pressure on the drivers, compromising their safety. Therefore, the industry wants to make the job easier by providing AI-based assistance to the drivers, making roads safer, and the delivery of goods faster.
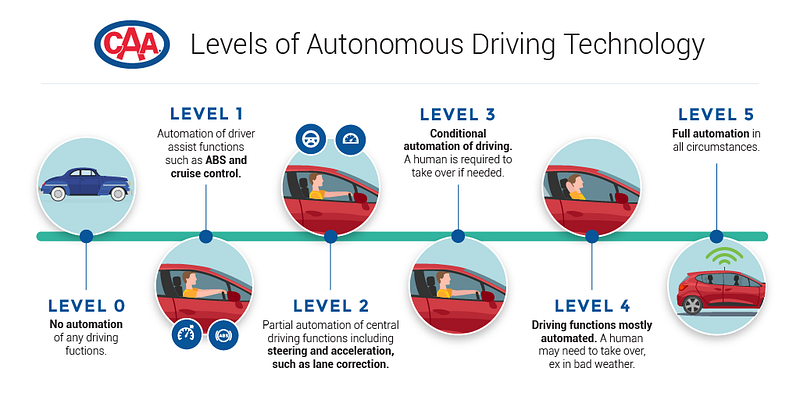
Autonomous Vehicles are judged based on a classification system published by SAE International, an automotive standardization body. In the system, the degree of autonomy of a vehicle is judged based on six levels — ranging from fully manual to fully automated system, which is based on the amount of driver intervention and attentiveness required.
Currently, the highest levels achieved are Level 3, achieved by system’s like Cadillac’s Super Cruise System, Audi’s A8, and Tesla’s autopilot system.
Some of the companies working to build solutions for autonomous vehicles are Waymo, Cruise and Tesla.
Waymo

One of the companies making exciting progress in the field of Autonomous Vehicles is Waymo. This Alphabet subsidiary is famous for offering the first true driverless ride-hailing service in the form of ‘Waymo One’, a limited robotaxi service.
This service started in April 2017, offering pickup & drop services to vetted users within a certain area in Phoenix. Although the rides initially had human drivers for ride safety and assistance, Waymo has since 2018 thought their automated system safe enough for rides with drivers being absent, offering riders-only (i.e. driverless) taxi services.
The self-driving features of a Waymo vehicle are powered by a series of sensors. These include Lidars, Cameras and Radar devices. Lidars are Light Detection and Ranging sensors, which allow a system to measure distances to various points in the environment by using a pulsed laser. Distances are measure by the reflected laser’s return times on objects and surfaces. So LIDARs allow Waymo’s system to paint an accurate map of the surroundings, regardless of time of day.
Waymo also uses camera sensors. Long-range camera sensors are used to detect far-off obstacles, pedestrians and stop signs. Concurrently, there are a series of shorter-range perimeter and peripheral sensors which provide the system with a more accurate representation of nearby objects, and reduces blindspots caused by parked or large vehicles.
Lastly, RADAR sensors are used to complement the other sensors, providing the ability to see and measure an object’s velocity even in tough weather conditions such as rain, fog, and snow.
By March of 2019, Waymo had above 600 vehicles on the streets of Arizona, as corroborated by this article.
Cruise

Another company making good progress in the Autonomous Vehicles industry is Cruise. Starting as a Y-Combinator startup, Cruise was focused on building direct-to-consumer kits to retrofit existing vehicles with self-driving capabilities. Cruise later shifted its focus to building software to be used by self driving cars. After, being acquired by GM, their primary focus and business model has been to develop software for making GM’s Chevy Bolt electric vehicle fully autonomous.
On Jan 21, 2020, Cruise revealed the first fully driverless vehicle — one without steering wheel or pedals — called Cruise Origin. Cruise’s leadership is vocally against individual ownership of cars, due to its safety and environment issues, and so, Cruise’s mission is to build a fleet of “shared-property” vehicles for use by everyone.
Although Cruise has been secretive with their technology, one can get a description of it through observations made by journalists. Their technology involves LIDARs, cameras and RADARs to form an image of the environment. The hard drive, stored in the trunk and housing the vehicle’s artificial intelligence and perception software, is cooled by the vehicle’s battery system, making it quieter and less prone to overheating.
As of July of 2019, Cruise had more than 180 vehicles on road, according to a report by CNBC.
Tesla

Tesla is the name that most people are familiar with in the field of Autonomous Vehicles. Their goal from the start was to build an electric vehicles company. The plan was to move from low-volume, high price electric vehicles, like the Tesla Roadster towards high-volume, low price vehicles like the Model 3. Tesla has a 3-pronged business model:
- Car Sales: Being an electric vehicles company, this is the main economic source of Tesla.
- Services and Service Centers: Tesla figured out that when they set up a service center in a new area or city, their sales were positively affected for the region. This was because the public could more easily service or charge their Tesla at these service locations.
- Supercharger network: The Tesla supercharger network are a series of electric vehicle charging points throughout the Unites States and some other countries which are available for Teslas to charge for a service fee. These have the same effect as increased service centers in increasing sales in an area.
Tesla’s Autopilot system was also one of the first commercially available Autonomous systems open to the general public. The system has a suite of advanced driver-assistance features like lane centering, adaptive cruise control, self-parking, the ability to automatically change lanes, navigate autonomously on freeways, and the ability to summon the car to and from a garage or parking spot. However, for all of these features, the driver is deemed responsible and recommended to have constant supervision over the car.
According to Tesla’s director of Artificial Intelligence Andrej Karpathy, Tesla had developed large neural networks for Autopilot that could not be used due to the lack of computational resources in the then current Tesla hardware. Hardware 3 provided the resources to allow for improved accuracy in predictions. It includes a custom Tesla-designed system on a chip.
Tesla claimed that the new system would process 2,300 frames per second (fps), which is a 21x improvement in image processing compared to the previous version. The firm described it as a “neural network accelerator”. The first availability of Hardware 3 was from April 2019. HW3 features twelve ARM Cortex-A72 CPUs operating at 2.6 GHz, two Neural Network Accelerators operating at 2 GHz and a Mali GPU operating at 1 GHz.
For physical sensors, Tesla uses cameras for computer vision and RADARs to sense the speed and distance between objects. Tesla does not use LIDAR technology. This is because LIDARs are expensive sensors, which make commercial autonomous vehicles unaffordable to the public, according to Elon Musk.
About future developments, Tesla’s CEO Elon Musk is of the opinion that full autonomy is “really a software limitation: The hardware exists to create full autonomy, so it’s really about developing advanced, narrow AI for the car to operate on.”
Tesla, being a commercial electric vehicle company, has a large amount of vehicles on street. They have about 730,000 vehicles with newer autopilot systems as of 2019 according to some reports.
We hope that this article was useful for you in learning about Autonomous Vehicles and the major companies working in the field.
Subscribe to read more articles related to Data Science & AI! We will be writing about more companies who’ve done great work in the field of data science & autonomous vehicles. If there is a company that you think we missed or if you want us to include a specific company in the next article, be sure to reach out to us.

